
Classify discrete word problems by their distributions.Calculate and interpret expected values.You can think of the complement rule as the ‘subtraction rule’ if it helps you to remember it. There are three main rules associated with basic probability: the addition rule, the multiplication rule, and the complement rule.
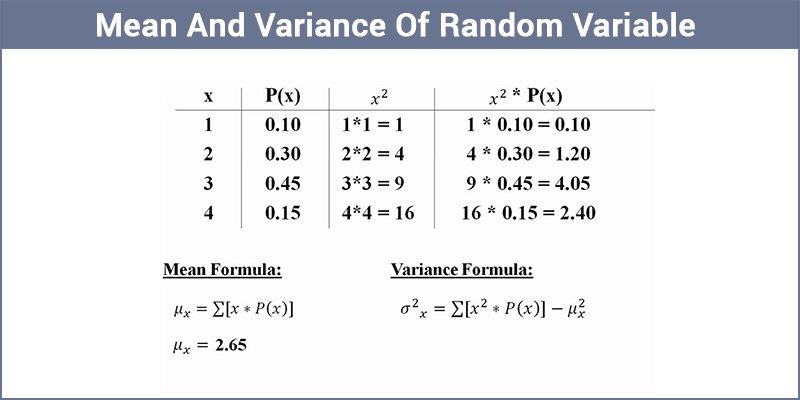
What are the four basic rules of probability? ) If A and B are independent, then P(A|B)=P(A) P ( A | B ) = P ( A ). (The probability of A given B equals the probability of A and B divided by the probability of B. If A and B are two events defined on a sample space, then: P(A AND B)=P(B)P(A|B) P ( A AND B ) = P ( B ) P ( A | B ). The conditional probability of an event B is the probability that the event will occur given the knowledge that an event A has already occurred. The result of any random experiment is called an outcome. Example- rolling a die, tossing a coin, and drawing a card from a deck are all examples of random experiments. Probability is the prediction of a particular outcome of a random event. The sample space S for a probability model is the set of all possible outcomes. It is defined by its sample space, events within the sample space, and probabilities associated with each event. What are probability models?Ī probability model is a mathematical representation of a random phenomenon. For example, the probability of flipping a coin and it being heads is ½, because there is 1 way of getting a head and the total number of possible outcomes is 2 (a head or tail). Probability = the number of ways of achieving success.
Converting the fraction 35 to a decimal, we would say there is a 0.6 probability of choosing a banana. The probability of an event is the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of outcomes possible. How do you find the probability of an OR event? Union The union of two sets A and B, written A U B, is the combination of the two sets. How do you find the normal probability curve? … The normal distribution is often called the bell curve because the graph of its probability density looks like a bell. The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is symmetrical on both sides of the mean, so the right side of the center is a mirror image of the left side. Subtract the average of the sample means from each value in the set. Probability Rule Four (Addition Rule for Disjoint Events)Ĭalculate the standard deviation of the distribution. Probability Rule Three (The Complement Rule) Probability Rule Two (The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes is 1) Probability Rule One (For any event A, 0 ≤ P(A) ≤ 1) There are three major types of probabilities: If the probability of one event doesn’t affect the other, you have an independent event. … Formula for the probability of A and B (independent events): p(A and B) = p(A) * p(B).
The probability of A and B means that we want to know the probability of two events happening at the same time. What are the four basic rules of probability?.How do you find the probability of an OR event?.How do you find the probability between two percentages?.How do you calculate independent probability?.Why do we calculate standard deviation?.How do you find the mean deviation Example?.What is standard deviation formula with example?.How do you find the normal probability curve?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
